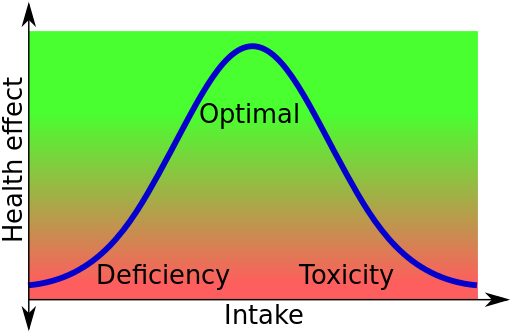
Will zinc prevent or reduce a cold?
A friend with kids who just went back to school asked me about using various zinc products to reduce the length of or prevent the common cold. Years ago, I tried the nasal swab version of one of these products (Zicam) and was amazed at how painful they were. This prompted me to research the … Read more